Note: I refer to this article all the time, so I’ve decided to mirror it here on my site. It comes from the now-defunct Debian Administration website.
A simple introduction to working with LVM
Posted by Steve on Wed 28 Jun 2006 at 21:22
The logical volume manager allows you to create and manage the storage of your servers in a very useful manner; adding, removing, and resizing partitions on demand. Getting started with LVM can be a little confusing to newcomer so this guide intends to show the basics in a simple manner.
There several pieces of terminology that you’ll need to understand to make the best use of LVM. The most important things you must know are:
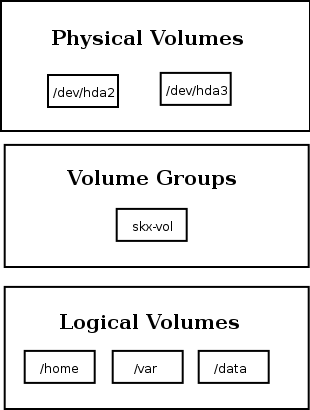
- physical volumes
- These are your physical disks, or disk partitions, such as /dev/hda or /dev/hdb1. These are what you’d be used to using when mounting/unmounting things. Using LVM we can combine multiple physical volumes into volume groups.
- volume groups
- A volume group is comprised of real physical volumes, and is the storage used to create logical volumes which you can create/resize/remove and use. You can consider a volume group as a “virtual partition” which is comprised of an arbitary number of physical volumes.
- logical volumes
- These are the volumes that you’ll ultimately end up mounting upon your system. They can be added, removed, and resized on the fly. Since these are contained in the volume groups they can be bigger than any single physical volume you might have. (ie. 4x5Gb drives can be combined into one 20Gb volume group, and you can then create two 10Gb logical volumes.)
Logically these are stacked from top to bottom like this:
Creating A Volume Group
To use LVM you need to take at least one partition, initialise it for use with LVM and then include it in a volume group. Why would you do this? Well it would let you create new partitions on the fly, and make better use of your space.
In my case I have a laptop with the following setup:
Name Flags Part Type FS Type [Label] Size (MB)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
hda1 Boot Primary Linux ext3 [/] 8000.01
hda2 Primary Linux swap / Solaris 1000.20
hda3 Primary Linux 31007.57
Here I have a 7Gb root partition which contains my Debian GNU/Linux installation. I also have a 28Gb partition which will be used by LVM. I’ve chosen this setup so that I can create a dedicated /home partition using LVM – and if I need more space I can extend it.
In this example hda1, hda2, and hda3 are all physical volumes. We’ll initialize hda3 as a physical volume:
root@lappy:~# pvcreate /dev/hda3
If you wanted to combine several disks, or partitions you could do the same for those:
root@lappy:~# pvcreate /dev/hdb root@lappy:~# pvcreate /dev/hdc
Once we’ve initialised the partitions, or drives, we will create a volume group which is built up of them:
root@lappy:~# vgcreate skx-vol /dev/hda3
Here “skx-vol” is the name of the volume group. (If you wanted to create a single volume spanning two disks you’d run “vgcreate skx-vol /dev/hdb /dev/hdc“.)
If you’ve done this correctly you’ll be able to see it included in the output of vgscan:
root@lappy:~# vgscan Reading all physical volumes. This may take a while... Found volume group "skx-vol" using metadata type lvm2
Now that we have a volume group (called skx-vol) we can actually start using it.
Working with logical volumes
What we really want to do is create logical volumes which we can mount and actually use. In the future if we run out of space on this volume we can resize it to gain more storage. Depending on the filesystem you’ve chosen you can even do this on the fly!
For test purposes we’ll create a small volume with the name ‘test’:
root@lappy:~# lvcreate -n test --size 1g skx-vol Logical volume "test" created
This command creates a volume of size 1Gb with the name test hosted on the LVM volume group skx-vol.
The logical volume will now be accessible via /dev/skx-vol/test, and may be formatted and mounted just like any other partition:
root@lappy:~# mkfs.ext3 /dev/skx-vol/test root@lappy:~# mkdir /home/test root@lappy:~# mount /dev/skx-vol/test /home/test
Cool, huh?
Now we get onto the fun stuff. Let us pretend that the test partition is full and we want to make it bigger. First of all we can look at how big it is at the moment with lvdisplay:
root@lappy:~# lvdisplay --- Logical volume --- LV Name /dev/skx-vol/test VG Name skx-vol LV UUID J5XlaT-e0Zj-4mHz-wtET-P6MQ-wsDV-Lk2o5A LV Write Access read/write LV Status available # open 0 LV Size 1.00 GB Current LE 256 Segments 1 Allocation inherit Read ahead sectors 0 Block device 254:0
We see it is 1Gb in size (no suprise really!) before we go on to resize the volume remember we should unmount it first:
root@lappy:~# umount /home/test/ root@lappy:~# lvextend -L+1g /dev/skx-vol/test Extending logical volume test to 2.00 GB Logical volume test successfully resized
(It is possible to resize ext3 filesystems whilst they’re mounted, but I’d still suggest doing it offline as that is less scary.)
Looking at lvdisplay again we can see the volume was resized:
root@lappy:~# lvdisplay --- Logical volume --- LV Name /dev/skx-vol/test VG Name skx-vg LV UUID uh7umg-7DqT-G2Ve-nNSX-03rs-KzFA-4fEwPX LV Write Access read/write LV Status available # open 0 LV Size 2.00 GB Current LE 512 Segments 1 Allocation inherit Read ahead sectors 0 Block device 254:0
The important thing to realise is that although the volume has been resized the ext3 filesystem on it has stayed unchanged. We need to resize the filesystem to actually fill the volume:
root@lappy:~# e2fsck -f /dev/skx-vol/test root@lappy:~# resize2fs /dev/skx-vol/test
Remount the logical volume and you’ll discover it is now only half full instead of completely full!
If you get bored of the volume and its contents you can remove it with the lvremove command:
root@lappy:~# lvremove /dev/skx-vol/test Do you really want to remove active logical volume "test"? [y/n]: y Logical volume "test" successfully removed
Other userful commands include lvrename to change the name, and lvreduce to reduce the size of a volume.
Mounting Logical Volumes
In the previous section we showed how you could mount a logical volume, with a command like this:
mount /dev/skx-vol/test /home/test
If you want your partition to be mounted at boot-time you should update your /etc/fstab to contain an entry like this:
/dev/skx-vol/home /home ext3 noatime 0 2 /dev/skx-vol/backups /backups ext3 noatime 0 2
Meta-Data
If you’re worried about losing details about your volumes in the event of problems do not worry. The current state of the LVM setup upon your machine is maintained in the event of errors.
Running pvdisplay will allow you to see which physical volume(s) make up your volume group. In the case of our example we only used /dev/hda3, but if you’re using more volumes it might be useful to take a look at them with the pvdisplay command:
root@lappy:~# pvdisplay --- Physical volume --- PV Name /dev/hda3 VG Name skx-vol PV Size 28.88 GB / not usable 0 Allocatable yes PE Size (KByte) 4096 Total PE 7392 Free PE 5280 Allocated PE 2112 PV UUID WyXQtL-OdT6-GnGd-edKF-tjRU-hoLA-RJuQ6x
If we ever lost this information we could find it contained in the file /etc/lvm/backup/skx-vol.
Similarly if we wanted to know which logical volumes we’d created we could example the directory /etc/lvm/archive. This contains numbered files containing backups of the operations we’ve conducted.
As an example we created the “test” volume, which we went on to resize. Here is the first section of /etc/lvm/archive/skx-vol_000009.vg:
# Generated by LVM2: Sat Jun 10 12:35:57 2006 contents = "Text Format Volume Group" version = 1 description = "Created *before* executing 'lvcreate -n test --size 1g skx-vg'" creation_host = "lappy" # Linux lappy 2.6.8-2-686 #1 Sat Jan 8 16:50:08 EST 2005 i686
Filesystems
When it comes to using LVM effectively it is worth considering the filesystem that you wish to use upon your logical volumes.
If you choose a filesystem which doesn’t support resizing then increasing the size of your LVM volumes would be pointless. Here is a brief list of the resizable filesystems:
filesystem increase while mounted increase while unmounted decrease ext2fs yes yes yes ext3fs yes yes yes ReiserFS yes yes yes JFS no no no XFS yes no no
Note that some filesystems can be increased in size, but cannot be reduced.
If I’ve missed one you’re familiar with please do let me know.
Closing Comments
If you’re ready to make the jump to LVM and don’t have a lot of space handy for allocating to LVM then it might make sense to reinstall your system. The Debian installer has excellent support for creating LVM setups.
We’ve not really covered advanced usage in this introduction but there is a lot of readable and useful documentation available if you’re prepared to search for it. The most obvious starting point is the LVM howto.